一、 概念
Apache 的 Thrift 软件框架,是用来进行可伸缩的、跨语言的服务开发,它通过一个代码生成引擎来构建高效、无缝的服务,这些服务能够实现跨语言调度,目前支持的语言有很多。
二、 安装Thrift
http://thrift.apache.org/download
Windows 直接下载 thrift.exe
Mac 用 brew 安装:
brew install thrift thrift -version
安装 python 模块(代码中要用的)
pip install thrift pip install apscheduler
三、 Thrift 支持的类型
1. 基本类型
bool:布尔值(true 或者 false)
byte:8位的有符号字节(java 的 byte 类型)
i16:16位的有符号整数(java 的 short 类型)
i32:32位的有符号整数(java 的 int 类型)
i64:64位的有符号长整型(java 的 long 类型)
double:一个64位的浮点数(java 的 double 类型)
string:一个utf8编码的字符串文本(java 的 String 类型)
2. Structs
Thrift 的 structs 用来定义一个通用对象,但是没有继承关系。
3. 集合类型
list:一个有序的元素列表。元素可以重复。
set:一个无序的元素集合,集合中元素不能重复。
map:一个键值对的数据结构,相当于Java中的HashMap。
4. 异常类型 Exceptions
Thrift 的异常类型,除了是继承于静态异常基类以外,其他的跟 struct 是类似的,表示的是一个异常对象。
5. 服务类型 Services
Thrift 的 service 类型相当于定义一个面向对象编程的一个接口。
Thrift 的编译器会根据这个接口定义来生成服务端和客户端的接口实现代码。
四、一个简单的 Thrift 调用实例
1. 编写 .thrift 文件,也就是 IDL(接口描述语言)文件
shared.thrift
namespace java shared
namespace python shared
struct SharedStruct {
1: i32 key
2: string value
}
service SharedService {
SharedStruct getStruct(1: i32 key)
}
tutorial.thrift
include "shared.thrift"
namespace java tutorial
namespace python tutorial
typedef i32 MyInteger
const i32 INT32CONSTANT = 9853
const map<string,string> MAPCONSTANT = {'hello':'world', 'goodnight':'moon'}
enum Operation {
ADD = 1,
SUBTRACT = 2,
MULTIPLY = 3,
DIVIDE = 4
}
struct Work {
1: i32 num1 = 0,
2: i32 num2,
3: Operation op,
4: optional string comment,
}
exception InvalidOperation {
1: i32 whatOp,
2: string why
}
service Calculator extends shared.SharedService {
void ping(),
i32 add(1:i32 num1, 2:i32 num2),
i32 calculate(1:i32 logid, 2:Work w) throws (1:InvalidOperation ouch),
oneway void zip()
}
2. 使用 thrift 的编译器,生成 Python 客户端和服务端的代码:
thrift.exe -r --gen py .\thr\shared.thrift thrift.exe -r --gen py .\thr\tutorial.thrift
在当前目录下生成 gen-py 文件夹,文件结构如下:
gen-py -- __init__.py -- shared -- -- __init__.py -- -- constants.py -- -- SharedService.py -- -- SharedService-remote -- -- ttypes.py -- tutorial -- -- __init__.py -- -- Calculator.py -- -- Calculator-remote -- -- constants.py -- -- ttypes.py
3. Thrift 的调用
服务端 pyServer.py 代码:
#coding:utf-8
from tutorial import Calculator
from tutorial.ttypes import *
from shared.ttypes import SharedStruct
from thrift.transport import TSocket
from thrift.transport import TTransport
from thrift.protocol import TBinaryProtocol
from thrift.server import TServer
class CalculatorHandler:
'''类中定义的方法用于实现在thrift文件中定义的接口'''
def __init__(self):
self.log = {}
def ping(self):
print('ping()')
def add(self, n1, n2):
print('add(%d,%d)' % (n1, n2))
return n1+n2
def calculate(self, logid, work):
print('calculate(%d, %r)' % (logid, work))
if work.op == Operation.ADD:
val = work.num1 + work.num2
elif work.op == Operation.SUBTRACT:
val = work.num1 - work.num2
elif work.op == Operation.MULTIPLY:
val = work.num1 * work.num2
elif work.op == Operation.DIVIDE:
if work.num2 == 0:
x = InvalidOperation()
x.whatOp = work.op
x.why = 'Cannot divide by 0'
raise x
val = work.num1 / work.num2
else:
x = InvalidOperation()
x.whatOp = work.op
x.why = 'Invalid operation'
raise x
log = SharedStruct()
log.key = logid
log.value = '%d' % (val)
self.log[logid] = log
return val
def getStruct(self, key):
print('getStruct(%d)' % (key))
return self.log[key]
def zip(self):
print('zip()')
# 实例化 Handler
handler = CalculatorHandler()
# 根据 handler 创建一个 processor
processor = Calculator.Processor(handler)
# 指定端口启动 transport
transport = TSocket.TServerSocket('127.0.0.1',port=9090)
# 创建 tfactory, pfactory
tfactory = TTransport.TBufferedTransportFactory()
pfactory = TBinaryProtocol.TBinaryProtocolFactory()
# 创建 Server
server = TServer.TSimpleServer(processor, transport, \
tfactory, pfactory)
# 以下都可用于创建多线程服务
# server = TServer.TThreadedServer(processor, transport, \
# tfactory, pfactory)
# server = TServer.TThreadPoolServer(processor, transport, \
# tfactory, pfactory)
print('Starting the server...')
server.serve()
print('done.')
客户端 pyClient.py 代码
#coding:utf-8
import time, datetime
from tutorial import Calculator
from tutorial.ttypes import *
from thrift import Thrift
from thrift.transport import TSocket
from thrift.transport import TTransport
from thrift.protocol import TBinaryProtocol
from apscheduler.schedulers.background import BackgroundScheduler
def doTask():
try:
# 连接 Socket
transport = TSocket.TSocket('localhost', 9090)
# 获取 Transport, 缓冲很重要,原始的socket非常慢
transport = TTransport.TBufferedTransport(transport)
# 获取 TBinaryProtocol,以协议形式包装
protocol = TBinaryProtocol.TBinaryProtocol(transport)
# 创建一个 Client,用于使用协议编码器
client = Calculator.Client(protocol)
# 连接通道 transport
transport.open()
client.ping()
print('ping()')
sum = client.add(1,1)
print('1+1=%d' % (sum))
work = Work()
work.op = Operation.DIVIDE
work.num1 = 1
work.num2 = 0
try:
quotient = client.calculate(1, work)
print('Whoa? You know how to divide by zero?')
except InvalidOperation as io:
print('InvalidOperation: %r' % io)
work.op = Operation.SUBTRACT
work.num1 = 15
work.num2 = 10
diff = client.calculate(1, work)
print('15-10=%d' % (diff))
log = client.getStruct(1)
print('Check log: %s' % (log.value))
# 关闭通道 transport
transport.close()
except Thrift.TException as tx:
print('%s' % (tx.message))
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 创建后台执行的 schedulers
scheduler = BackgroundScheduler()
# 添加调度任务
# 调度方法为 doTask,触发器选择 interval(间隔性),间隔时长为3秒
scheduler.add_job(doTask, 'interval', seconds=3)
# 启动调度任务
scheduler.start()
while True:
now = time.localtime(int(time.time()))
print(time.strftime('===== %Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S =====', now))
time.sleep(2)
先运行服务端,然后再运行客户端,观察服务端和客户端的输出来理解下thrift的一个调用流程是什么样的。
客户端运行的效果为(每隔3秒执行一次,每隔2秒打印时间):
>pyClient.py ping() 1+1=2 InvalidOperation: InvalidOperation(whatOp=4, why='Cannot divide by 0') 15-10=5 Check log: 5
服务端运行的效果为:
>pyServer.py Starting the server... ping() add(1,1) calculate(1, Work(num1=1, num2=0, op=4, comment=None)) calculate(1, Work(num1=15, num2=10, op=2, comment=None)) getStruct(1)
Java 版本代码:
pom.xml:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.thrift</groupId>
<artifactId>libthrift</artifactId>
<version>0.13.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.slf4j/slf4j-api -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>1.7.25</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/log4j/log4j -->
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
resources/log4j2.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Configuration status="WARN">
<Appenders>
<Console name="Console" target="SYSTEM_OUT">
<PatternLayout pattern="%d{HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%t] %-5level %logger{36} - %msg%n" />
</Console>
</Appenders>
<Loggers>
<Root level="info">
<AppenderRef ref="Console" />
</Root>
</Loggers>
</Configuration>
Java 客户端? JavaClient.java 代码:
import org.apache.thrift.TException;
import org.apache.thrift.protocol.TBinaryProtocol;
import org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TSSLTransportFactory;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TSSLTransportFactory.TSSLTransportParameters;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TSocket;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TTransport;
import shared.SharedStruct;
import tutorial.Calculator;
import tutorial.InvalidOperation;
import tutorial.Operation;
import tutorial.Work;
public class JavaClient {
public static void main(String [] args) {
if (args.length != 1) {
System.out.println("Please enter 'simple' or 'secure'");
System.exit(0);
}
try {
TTransport transport;
if (args[0].contains("simple")) {
System.out.println("thrift client connext server at 9090 port ");
transport = new TSocket("127.0.0.1", 9090);
transport.open();
}
else {
/*
* Similar to the server, you can use the parameters to setup client parameters or
* use the default settings. On the client side, you will need a TrustStore which
* contains the trusted certificate along with the public key.
* For this example it's a self-signed cert.
*/
TSSLTransportParameters params = new TSSLTransportParameters();
params.setTrustStore(JavaClient.class.getResource(".truststore").getPath(), "8384250", "SunX509", "JKS");
/*
* Get a client transport instead of a server transport. The connection is opened on
* invocation of the factory method, no need to specifically call open()
*/
transport = TSSLTransportFactory.getClientSocket("localhost", 9091, 0, params);
}
TProtocol protocol = new TBinaryProtocol(transport);
Calculator.Client client = new Calculator.Client(protocol);
perform(client);
transport.close();
} catch (TException x) {
x.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void perform(Calculator.Client client) throws TException
{
client.ping();
System.out.println("ping()");
int sum = client.add(1,1);
System.out.println("1+1=" + sum);
Work work = new Work();
work.op = Operation.DIVIDE;
work.num1 = 1;
work.num2 = 0;
try {
int quotient = client.calculate(1, work);
System.out.println("Whoa we can divide by 0");
} catch (InvalidOperation io) {
System.out.println("Invalid operation: " + io.why);
}
work.op = Operation.SUBTRACT;
work.num1 = 15;
work.num2 = 10;
try {
int diff = client.calculate(1, work);
System.out.println("15-10=" + diff);
} catch (InvalidOperation io) {
System.out.println("Invalid operation: " + io.why);
}
SharedStruct log = client.getStruct(1);
System.out.println("Check log: " + log.value);
}
}
Java 服务端代码:
JavaServer.java
import org.apache.thrift.server.TServer;
import org.apache.thrift.server.TServer.Args;
import org.apache.thrift.server.TSimpleServer;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TSSLTransportFactory;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TSSLTransportFactory.TSSLTransportParameters;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TServerSocket;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TServerTransport;
import tutorial.Calculator;
// Generated code
public class JavaServer {
public static CalculatorHandler handler;
public static Calculator.Processor processor;
public static void main(String [] args) {
try {
handler = new CalculatorHandler();
processor = new Calculator.Processor(handler);
Runnable simple = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
simple(processor);
}
};
Runnable secure = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
secure(processor);
}
};
new Thread(simple).start();
new Thread(secure).start();
} catch (Exception x) {
x.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void simple(Calculator.Processor processor) {
try {
TServerTransport serverTransport = new TServerSocket(9090);
TServer server = new TSimpleServer(new Args(serverTransport).processor(processor));
// Use this for a multithreaded server
// TServer server = new TThreadPoolServer(new TThreadPoolServer.Args(serverTransport).processor(processor));
System.out.println("Starting the simple server...");
server.serve();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void secure(Calculator.Processor processor) {
try {
/*
* Use TSSLTransportParameters to setup the required SSL parameters. In this example
* we are setting the keystore and the keystore password. Other things like algorithms,
* cipher suites, client auth etc can be set.
*/
TSSLTransportParameters params = new TSSLTransportParameters();
// The Keystore contains the private key
params.setKeyStore(JavaServer.class.getResource(".keystore").getPath(), "8384250", null, null);
/*
* Use any of the TSSLTransportFactory to get a server transport with the appropriate
* SSL configuration. You can use the default settings if properties are set in the command line.
* Ex: -Djavax.net.ssl.keyStore=.keystore and -Djavax.net.ssl.keyStorePassword=thrift
*
* Note: You need not explicitly call open(). The underlying server socket is bound on return
* from the factory class.
*/
TServerTransport serverTransport = TSSLTransportFactory.getServerSocket(9091, 0, null, params);
TServer server = new TSimpleServer(new Args(serverTransport).processor(processor));
// Use this for a multi threaded server
// TServer server = new TThreadPoolServer(new TThreadPoolServer.Args(serverTransport).processor(processor));
System.out.println("Starting the secure server...");
server.serve();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
CalculatorHandler.java
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
* or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
* distributed with this work for additional information
* regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
* to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
* "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
* with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,
* software distributed under the License is distributed on an
* "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY
* KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
* specific language governing permissions and limitations
* under the License.
*/
import shared.SharedStruct;
import tutorial.Calculator;
import tutorial.InvalidOperation;
import tutorial.Work;
import java.util.HashMap;
// Generated code
public class CalculatorHandler implements Calculator.Iface {
private HashMap<Integer,SharedStruct> log;
public CalculatorHandler() {
log = new HashMap<Integer, SharedStruct>();
}
public void ping() {
System.out.println("ping()");
}
public int add(int n1, int n2) {
System.out.println("add(" + n1 + "," + n2 + ")");
return n1 + n2;
}
public int calculate(int logid, Work work) throws InvalidOperation {
System.out.println("calculate(" + logid + ", {" + work.op + "," + work.num1 + "," + work.num2 + "})");
int val = 0;
switch (work.op) {
case ADD:
val = work.num1 + work.num2;
break;
case SUBTRACT:
val = work.num1 - work.num2;
break;
case MULTIPLY:
val = work.num1 * work.num2;
break;
case DIVIDE:
if (work.num2 == 0) {
InvalidOperation io = new InvalidOperation();
io.whatOp = work.op.getValue();
io.why = "Cannot divide by 0";
throw io;
}
val = work.num1 / work.num2;
break;
default:
InvalidOperation io = new InvalidOperation();
io.whatOp = work.op.getValue();
io.why = "Unknown operation";
throw io;
}
SharedStruct entry = new SharedStruct();
entry.key = logid;
entry.value = Integer.toString(val);
log.put(logid, entry);
return val;
}
public SharedStruct getStruct(int key) {
System.out.println("getStruct(" + key + ")");
return log.get(key);
}
public void zip() {
System.out.println("zip()");
}
}
五、Thrift 的架构原理
以下是 thrift 的客户端和服务端交互的一个原理图:
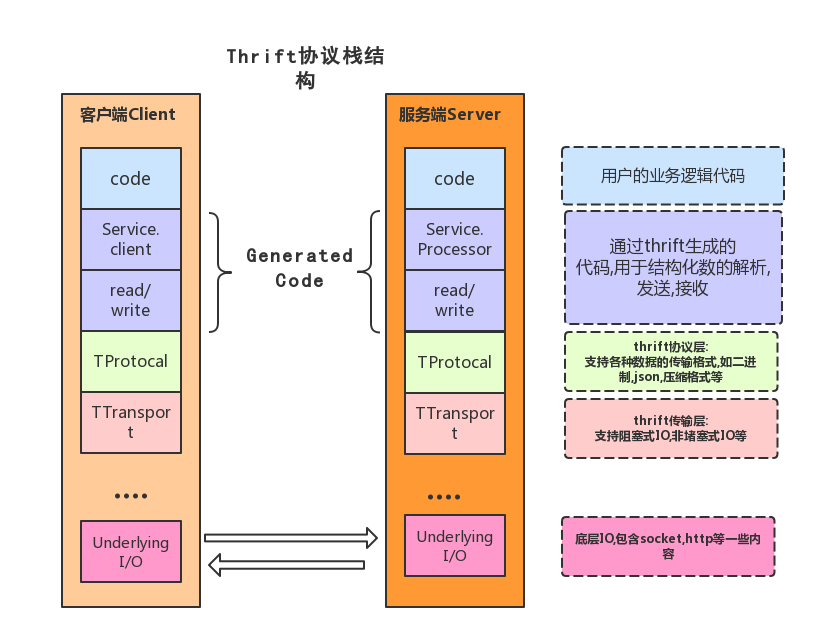
Thrift 的 RPC 调用的一个完整流程
如上图,客户端在进行远程方法调用时,首先是通过Thrift的编译器生成的客户端,将调用信息(方法名,参数信息)以指定的协议进行封装,而传输层 TTransport 是对协议层的封装进行处理(比如封装成帧 frame),并通过网络发送出去。
服务端流程跟客户端相反,收到客户端发过来的数据后,首先经过传输层对传过来的数据进行处理,然后使用特定的协议(跟客户端是一一对应的)进行解析,然后再通过生成的 Processor 调用用户编写的代码,如果有返回值的话,返回值以逆向的顺序,即通过协议层封装,然后传输层处理对数据进行发送,到了客户端那边就是对服务端返回的数据进行处理,使用特定协议进行解析,然后得到一个调用个的结果。
六、 Thrift 的传输格式(协议层)
Thrift之所以被称为一种高效的RPC框架,其中一个重要的原因就是它提供了高效的数据传输。
以下是Thrift的传输格式种类:
TBinaryProtocol: 二进制格式。效率显然高于文本格式。
TCompactProtocol:压缩格式。在二进制基础上进一步压缩。
TJSONProtocol:JSON 格式。
TSimpleJSONProtocol:提供 JSON 只写协议(缺少元数据信息),生成的文件很容易用过脚本语言解析。
TDebugProtocol:使用易懂的刻度文本格式,以便于调试。
以上可以看到,在线上环境,使用 TCompactProtocol 格式效率是最高的,同等数据传输占用网络带宽是最少的。
七、Thrift 的数据传输方式(传输层)
TSocket:阻塞式 socket。
TFramedTransport:以 frame 为单位进行传输,非阻塞式服务中使用。
TFileTransport:以文件形式进行传输。
TMemoryTransport:将内存用于 I/O,Java 是现实内部实际使用了简单的 ByteArrayOutputStream。
TZlibTransport:使用 zlib 进行压缩,与其他传输方式联合使用。当前无 java 实现。
八、Thrift的服务模型
TSimpleServer
简单的单线程服务模型,常用于测试。只在一个单独的线程中以阻塞 I/O 的方式来提供服务。所以它只能服务一个客户端连接,其他所有客户端在被服务器端接受之前都只能等待。
TNonblockingServer
它使用了非阻塞式I/O,使用了 java.nio.channels.Selector,通过调用 select(),它使得程序阻塞在多个连接上,而不是单一的一个连接上。TNonblockingServer 处理这些连接的时候,要么接受它,要么从它那读数据,要么把数据写到它那里,然后再次调用 select() 来等待下一个准备好的可用的连接。通用这种方式,server 可同时服务多个客户端,而不会出现一个客户端把其他客户端全部“饿死”的情况。缺点是所有消息是被调用 select() 方法的同一个线程处理的,服务端同一时间只会处理一个消息,并没有实现并行处理。
THsHaServer(半同步半异步server)
针对 TNonblockingServer 存在的问题,THsHaServer 应运而生。它使用一个单独的线程专门负责I/O,同样使用 java.nio.channels.Selector,通过调用 select()。然后再利用一个独立的 worker 线程池来处理消息。只要有空闲的 worker 线程,消息就会被立即处理,因此多条消息能被并行处理。效率进一步得到了提高。
TThreadedSelectorServer
它与THsHaServer的主要区别在于,TThreadedSelectorServer 允许你用多个线程来处理网络 I/O。它维护了两个线程池,一个用来处理网络I/O,另一个用来进行请求的处理。
TThreadPoolServer
它使用的是一种多线程服务模型,使用标准的阻塞式 I/O。它会使用一个单独的线程来接收连接。一旦接受了一个连接,它就会被放入 ThreadPoolExecutor? 中的一个 worker 线程里处理。worker 线程被绑定到特定的客户端连接上,直到它关闭。一旦连接关闭,该 worker 线程就又回到了线程池中。
这意味着,如果有1万个并发的客户端连接,你就需要运行1万个线程。所以它对系统资源的消耗不像其他类型的 server 一样那么“友好”。此外,如果客户端数量超过了线程池中的最大线程数,在有一个 worker 线程可用之前,请求将被一直阻塞在那里。
如果提前知道了将要连接到服务器上的客户端数量,并且不介意运行大量线程的话,TThreadPoolServer 可能是个很好的选择。
九、 其他
Facebook 开源了一个简化 thrift java 开发的一个库 —— swift。swift 是一个易于使用的、基于注解的 java 库,主要用来创建 thrift 可序列化类型和服务。
github地址:https://github.com/facebook/swift
十、 总结
Thrift 是一个跨语言的 RPC 框架,如果有跨语言交互的业务场景,Thrift 可能是一个很好的选择。如果使用恰当,thrift 将是一个非常高效的一个 RPC 框架。开发时应根据具体场景选择合适的协议,传输方式以及服务模型。缺点就是 Thrift 并没有像 dubbo 那样提供分布式服务的支持,如果要支持分布式,需要开发者自己去开发集成。
431 thoughts on “跨语言 RPC 框架 Thrift 详解(Python/Java篇)”